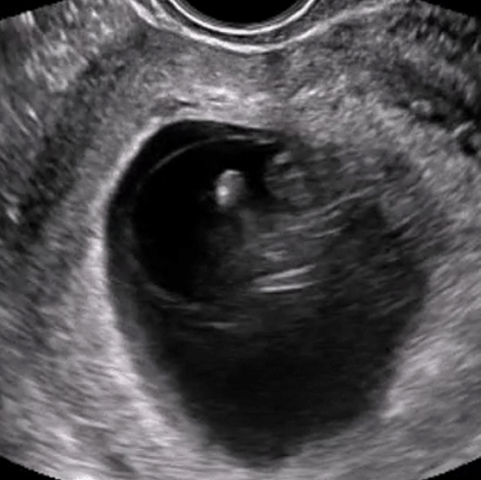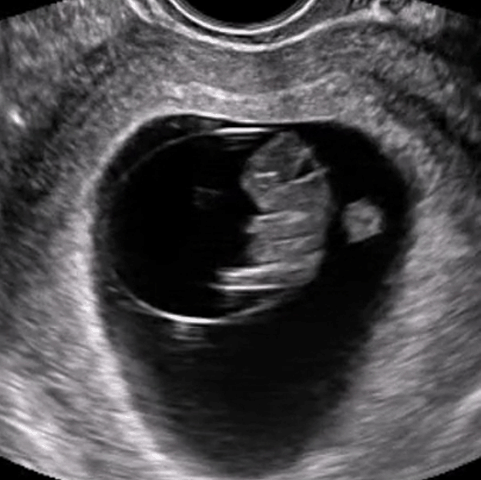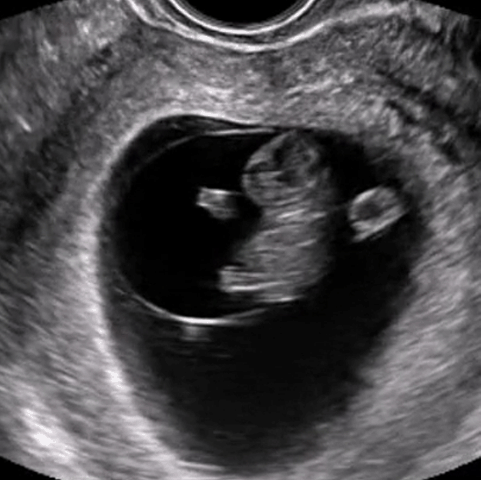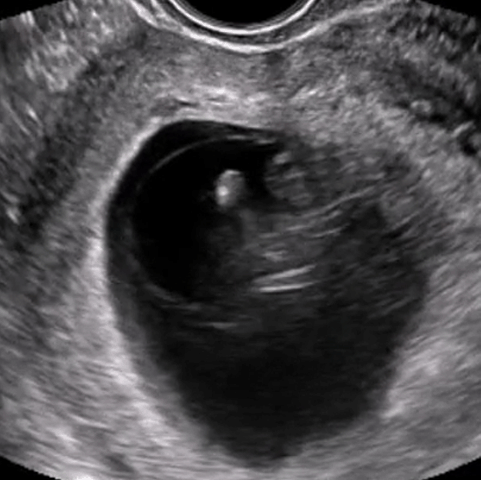
Virtual, Hands-On Ultrasound Scanning
The SonoSimulator®: Scan Real Pathology on Virtual Patients.
On Your Laptop. Anytime. Anywhere.
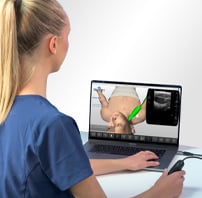
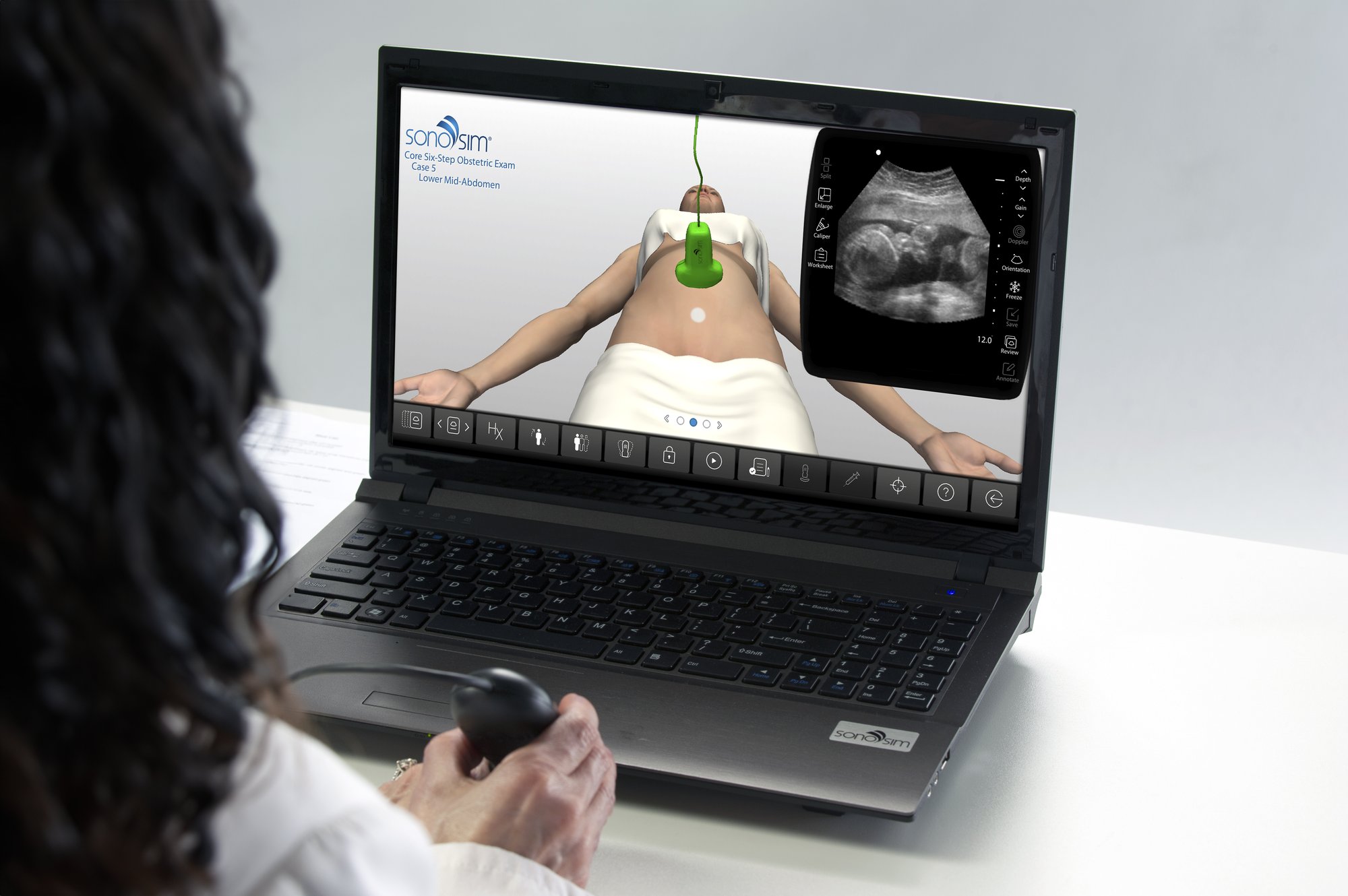
Gain practical experience in ultrasound scanning anytime, anywhere with our patented SonoSimulator software. The SonoSimulator overcomes the primary barriers to learning ultrasound, including access to patients with pathologic conditions, a qualified ultrasound instructor, an ultrasound machine, and repetitive practice until mastery. With on-demand access to thousands of pathologic scanning cases from real patients, learners are taught image acquisition and interpretation using any laptop computer. SonoSim probe positioning guidance, a virtual tutor, and immediate AI-based performance assessment and feedback support the ability to learn ultrasound quickly and efficiently.

Ultrasound Scanning on Virtual Patients with Real Anatomy
Unlock the full potential of ultrasound scanning with our innovative platform that addresses the traditional barriers to learning and teaching ultrasound. Our comprehensive case-based learning approach, constructed by ultrasound experts, leverages an on-screen tutor, virtual probe guide, and advanced training ultrasound modalities like Doppler. SonoSim helps you make it easier than ever for your learners to master ultrasound scanning skills, anytime and anywhere. Whether you're overseeing ultrasound education for a DMS program, medical school, residency program, or medical group, or maybe you are an individual healthcare practitioner interested in adding ultrasound skills to your practice - wherever you are in your ultrasound competency journey, our platform can help you overcome the traditional hurdles of learning ultrasound education. Simply put, SonoSim will more quickly and effectively teach the skills needed to put the power of ultrasound to work improving patient care.
The SonoSimulator®
Simulate Ultrasound Scanning. Anytime. Anywhere.
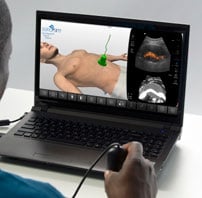
The SonoSimulator offers a robust simulated environment that provides hands-on ultrasound scanning practice on virtual patients with real pathologic cases. Integrating most of the features and functionality of real ultrasound machines, the SonoSimulator is a powerful tool for learning ultrasound scanning techniques in a risk-free virtual simulation. Using a proven approach, learners execute the exact fanning, rocking, and rotational movements of a real ultrasound machine exam to acquire the desired ultrasound image. With the SonoSimulator probe, learners practice proper probe positioning, scanning, and optimizing image acquisition. Learners are provided unlimited practice with on-demand expert assistance.
When paired with bedside clinical practice, this proven approach rapidly accelerates the development of ultrasound image acquisition and interpretation skills, not to mention confidence and self-sufficiency in the learners.
On-Screen Expertise, On-Demand
Tools Contained in the Software Help Instruct Learners in the Moment
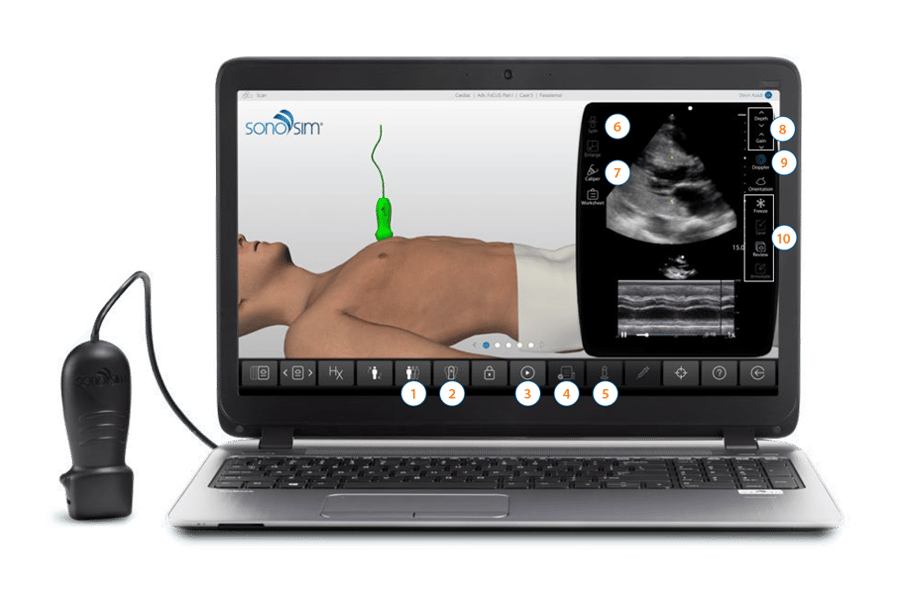

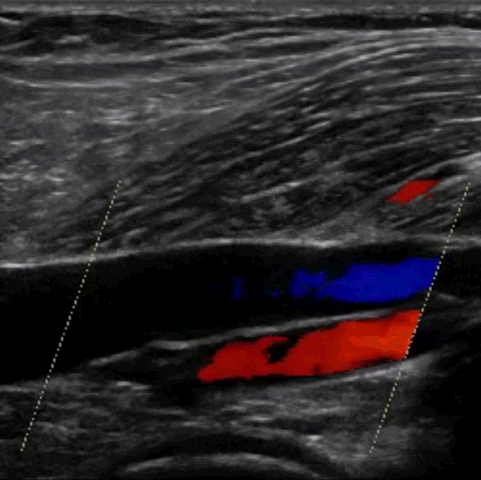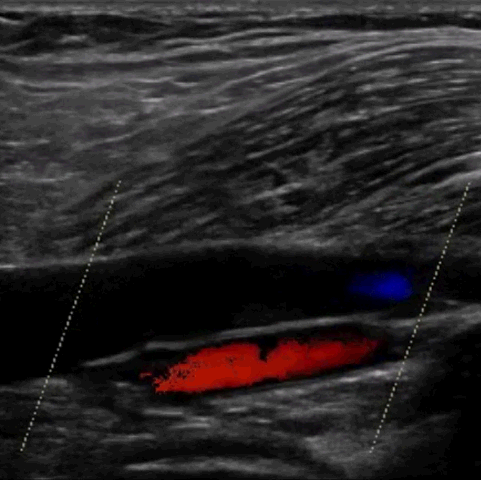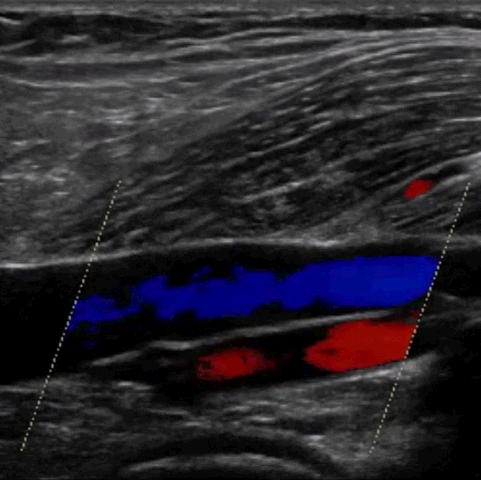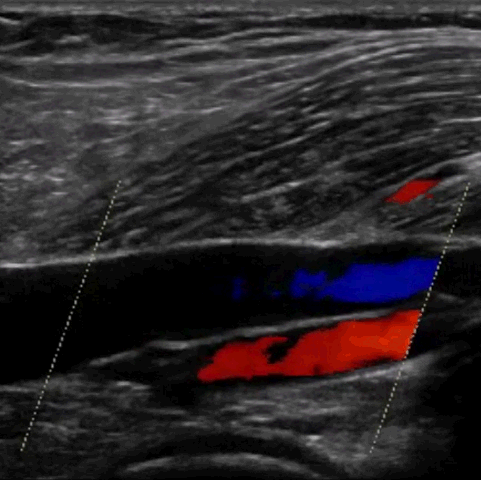
See the ultrasound beam transect underlying anatomy

Virtual probe helps learners align SonoSimulator Probe for optimal imaging

Image interpretation assistance from expert instructors

Disable virtual tutor features for assessment

Press & hold to simulate compression for structural evaluation

Compare co-registered image sets (CT, MRI, etc.) & review collateral imaging (X-rays, etc.)

Basic & application-specific calipers (e.g. OB) used to measure structures

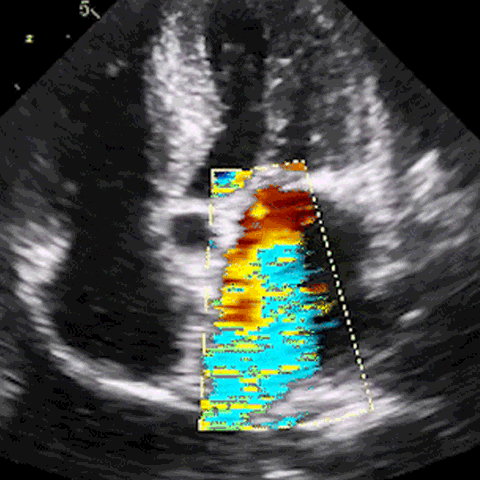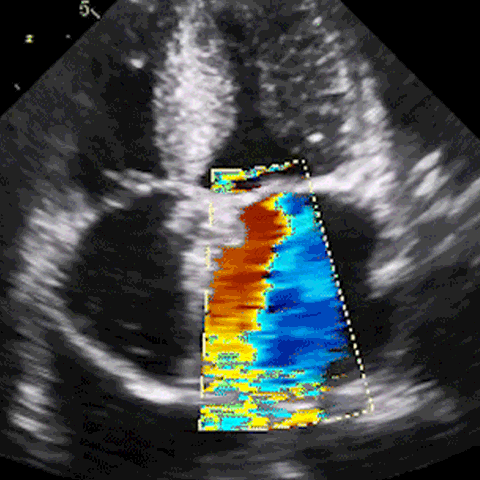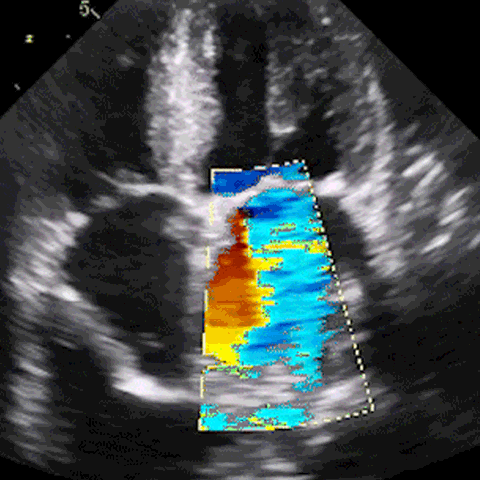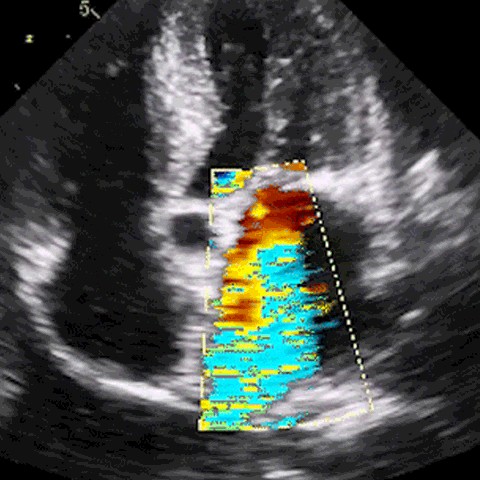
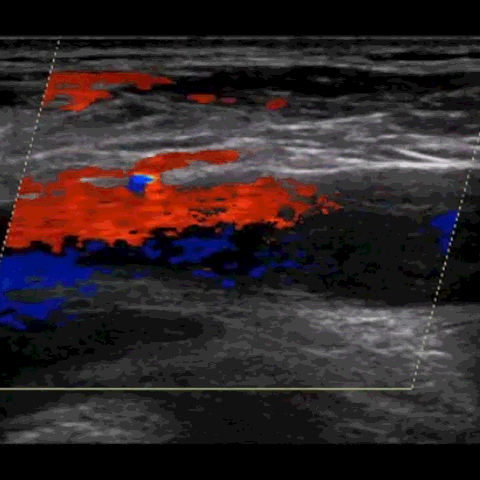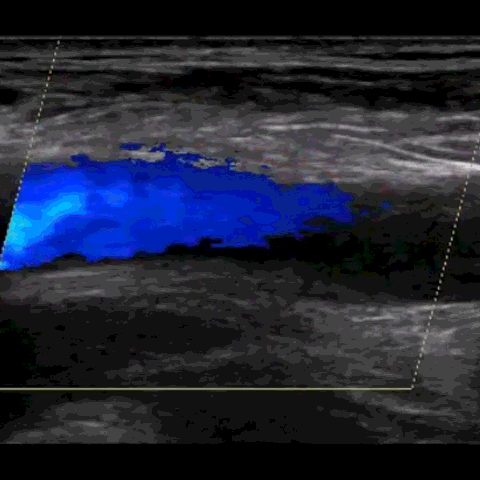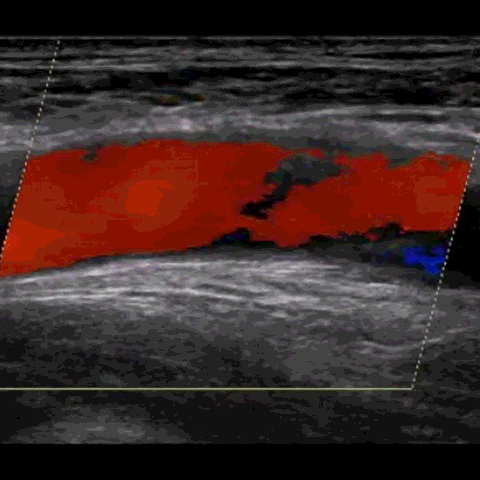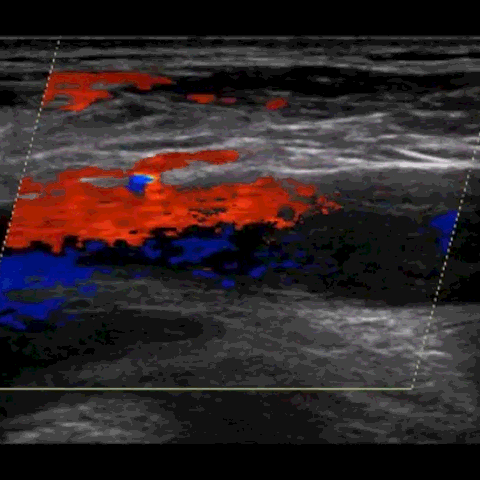
M-mode, CFD, PWD, & CWD

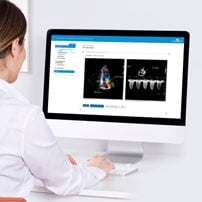
Data saved in SonoSim Performance Tracker

Adjust as needed
Get Expert Virtual Instruction at Critical Teaching Moments
On-Screen Probe Guide, On-Demand Virtual Tutor, Layer Removal & Immediate Feedback
Develop ultrasound image acquisition and interpretation skills with our patented SonoSimulator®. Our innovative platform provides hands-on practice with on-screen probe guide and virtual tutor on-demand overcoming the primary barriers to learning how to scan and read ultrasound.
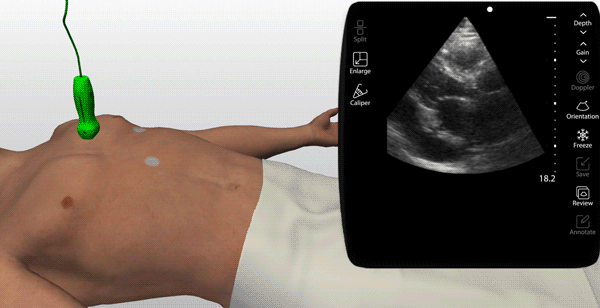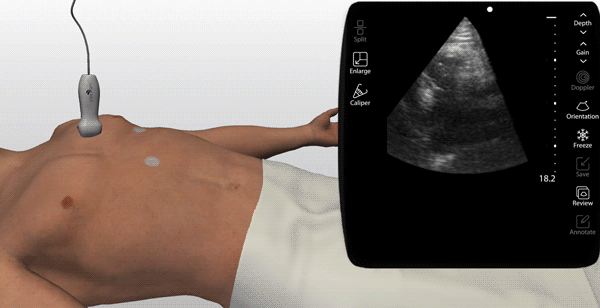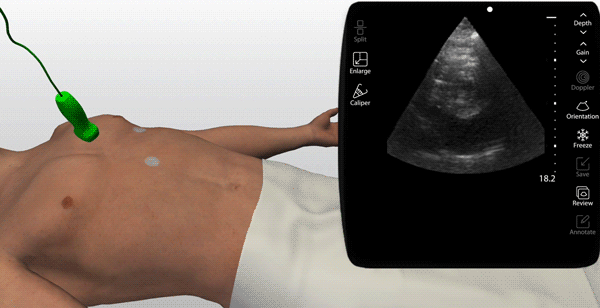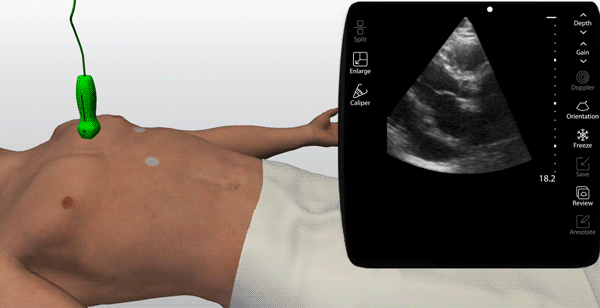
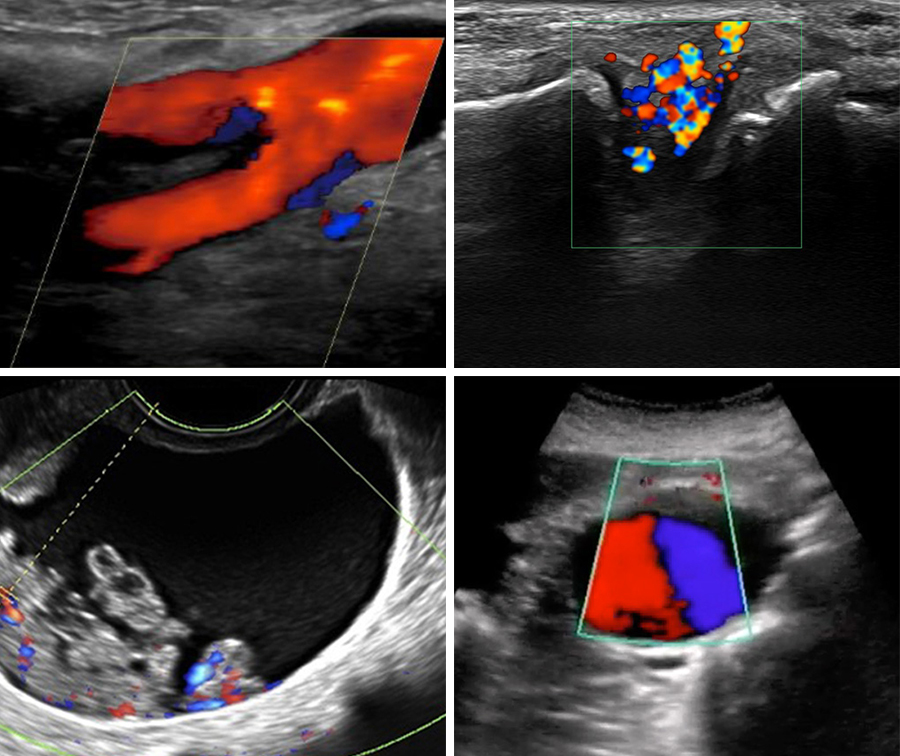
Choose from a thousand scanning cases from real patients (normal & pathologic)
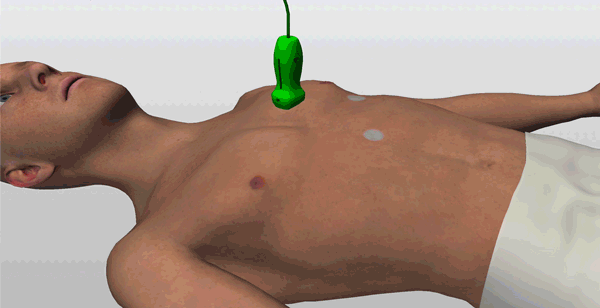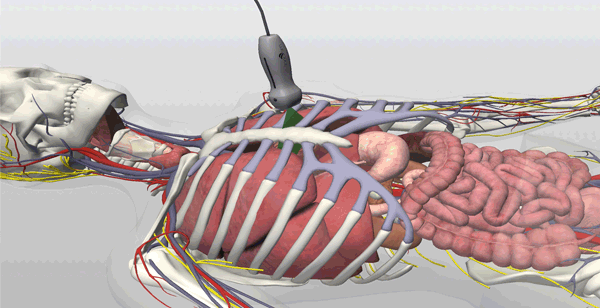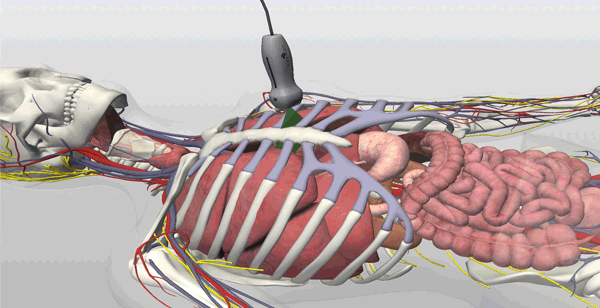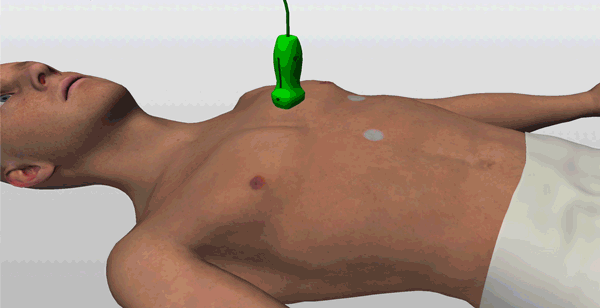
An on-screen probe guide provides precise image acquisition guidance & virtual layers help develop visuospatial skills
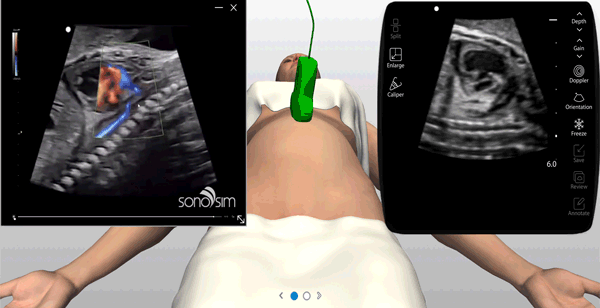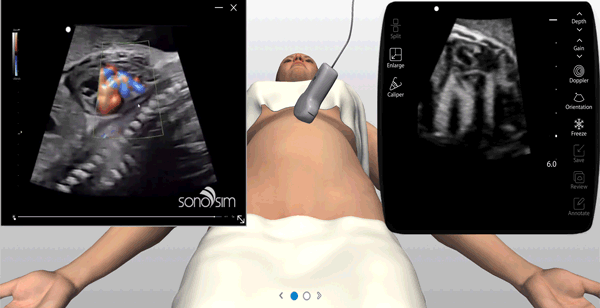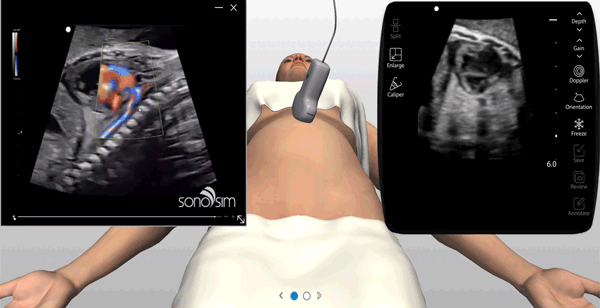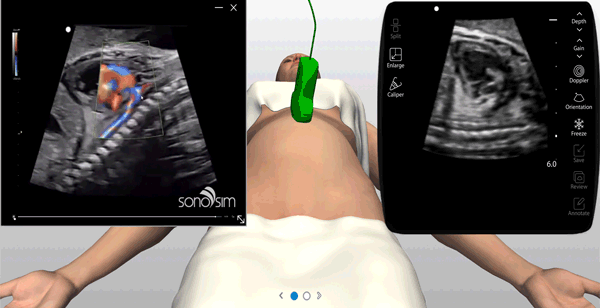
Ultrasound experts narrate key findings & provide imaging tips / real-time feedback
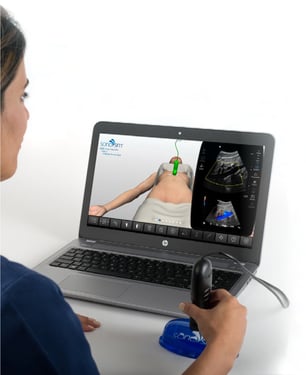
The SonoSimulator, compatible with any laptop, provides unlimited ultrasound scanning practice, so you can:
-
Gain experience with real pathological ultrasound scanning cases
-
Enhance your ultrasound image acquisition and interpretation expertise
-
Practice ultrasound anytime, anywhere with instruction tools on-demand
Scan Real Pathologic Cases On-Demand
Access an Extensive and Ever-Expanding Library of Ultrasound Cases
Unlimited ultrasound scanning opportunities with a diverse selection of real patient cases, such as:
Download Your Guide to Online Ultrasound Scanning - Get the Scan Brochure!
Enhance Your Ultrasound Scanning with the SonoSimulator.
FAQ
What is the SonoSimulator?
The SonoSimulator is a state-of-the-art simulation platform developed by SonoSim, designed to help medical professionals and students improve their ultrasound scanning skills. It offers a comprehensive and user-friendly learning experience, allowing users to practice on virtual patients, access a wide range of real-life pathologic cases, and receive guidance from an on-screen guide and virtual tutor. By using the SonoSimulator, learners can enhance their image acquisition, interpretation, and diagnostic abilities in a flexible, low-pressure environment.
Is this a real ultrasound probe?
No. SonoSim provides a patented SonoSimulator Probe which can be connected to your laptop where it controls the patented SonoSimulator software and all the thousands of scanning windows available for practice. Both pathology and normal cases of real patient can be accessed and scanned for practice as many times as you like. The SonoSimulator works very much like a real ultrasound machine but it is not a real ultrasound machine.
Can I scan a patient with this probe?
The SonoSimulator Probe is connected via USB to a laptop and simulation software is installed. The SonoSimulator Probe emulates the scanning capabilities of a real ultrasound probe for learning and teaching purposes. In this way, the simulation ultrasound probe lets the learner access pre-acquired ultrasound cases from real patients that are stored in the software, but doesn't scan real anatomy itself.
The SonoSim Ecosystem
Comprehensive Ultrasound Learning & Teaching
Flexible Learning Pathways
A Customizable Ecosystem for Every Program
80+ ultrasound courses, across a wide array of topics and learner levels - all accessible on-demand
A growing library of Challenge Cases futher develop ultrasound skills and provide exposure to important additional pathologies.
With SonoSim LiveScan® unlock the power of ultrasound in simulation through remote control of vital signs and pathophysiologic states in simulation.
Explore the SonoSim Ecosystem
Next Element - Practice
The SonoSim ecosystem is made up of 7 separate, yet complementary elements. Learn how each one plays a crucial role in helping you solve the ultrasound competency puzzle.