SonoSim kicks off quarter 2 with new content and features for all Members. Continue reading below to learn more:
New Procedure Module: Ultrasound-Guided Neonatal & Infant Lumbar Puncture
Case-Based Learning: New Challenge Case
New Admin Reporting: SPI Test Prep
New Procedure Module: Ultrasound-Guided Neonatal & Infant Lumbar Puncture
 .
. 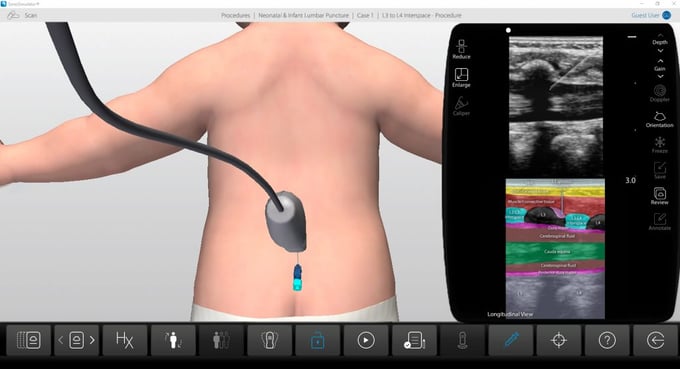
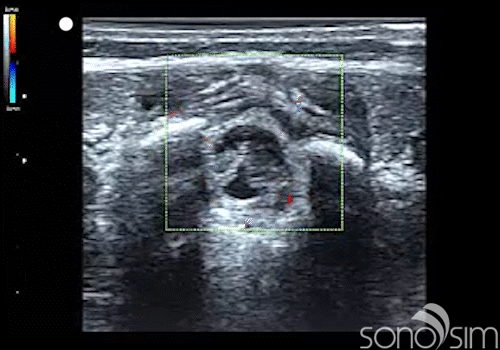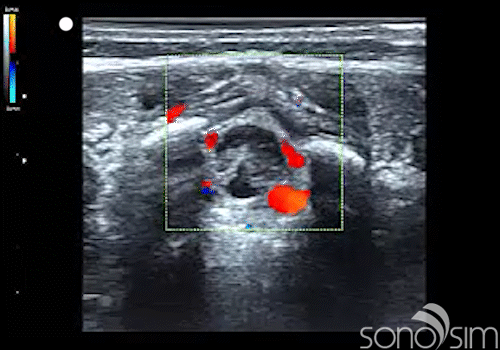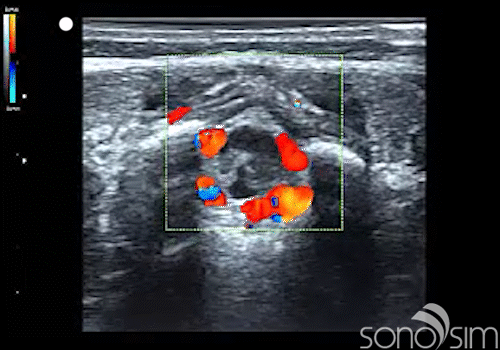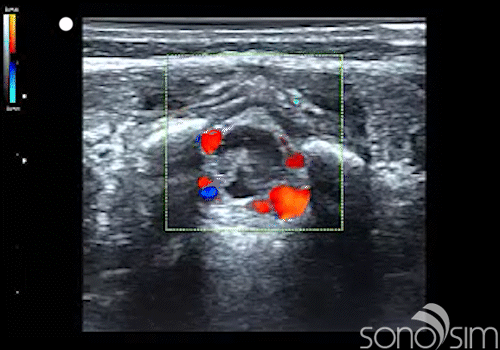
Case History: This 6-week-old female presents to the emergency department with a T = 39.5 C. Care providers decide to perform a lumbar puncture as part of the fever evaluation.
Learn the basic principles of performing ultrasound-guided neonatal and infant lumbar punctures. Review relevant anatomic landmarks and the use of ultrasound to evaluate the lumbosacral spine.
- The course covers topics including:
- Spinal Anatomy
- Sonography Anatomy & Characteristics
- Transducer Selection & Patient Positioning
- Survey Scan & Procedure Steps
- Tips, Pitfalls, & Complications
- Two real-patient based pediatric cases:
- Scanning Approaches: Dorsal approach to imaging from the conus medullaris thru the sacrum
- Procedural Techniques: In-plane & out-of-plane needle guidance approaches
- Color Doppler evaluation
*Each SonoSim Module consists of an online didactic course, in-course assessment questions, and a mastery test upon course completion. A scanning assignment that corresponds with real-patient hands-on scanning case(s) using the SonoSimulator®, SonoSim Performance Tracking, and Mobile App access to course content is also included.
Case-Based Learning: New Challenge Case
 .
. 
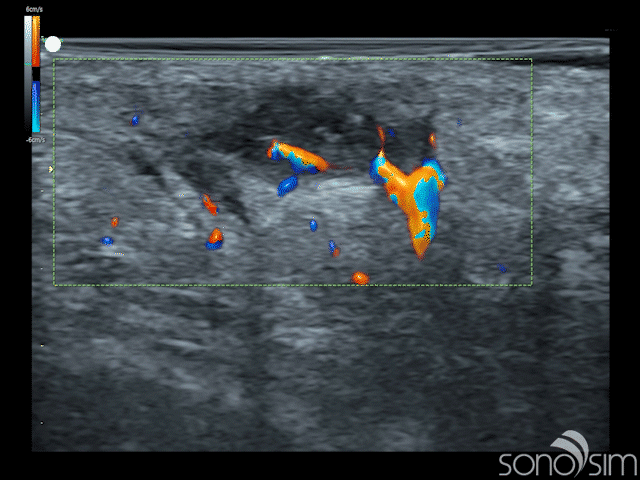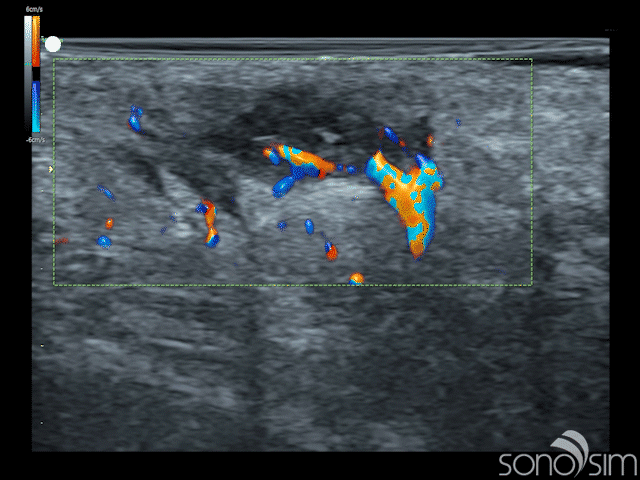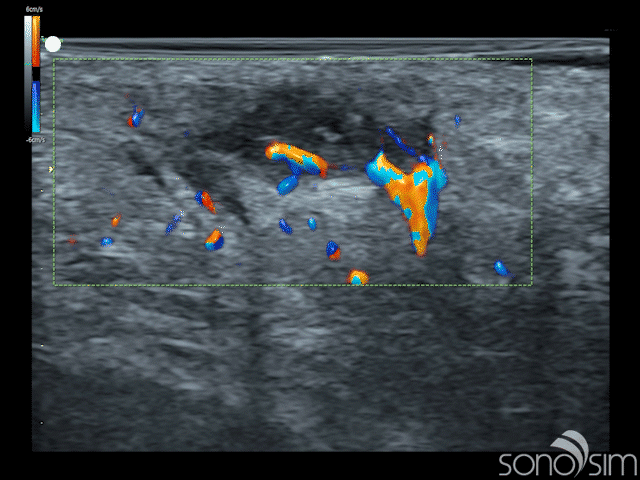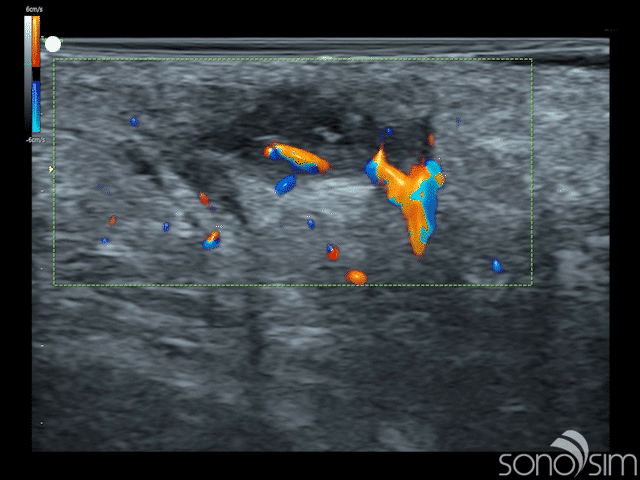
Case History: This is a 23-year-old female that presents with painful swelling in her right axillary region. She reports multiple similar past episodes, which had all self-resolved, and states that this episode is the worst to date. Physical examination reveals a localized, marble-sized region of painful, soft-tissue swelling.
Case-Based Learning via SonoSimulator scanning cases with unique pathologies will appear as “Challenge Cases”. This latest release delivers the following case:
- MSK Challenge Case 12
- Subcutaneous Abscess in Right Axilla
New Admin Reporting: SPI Test Prep
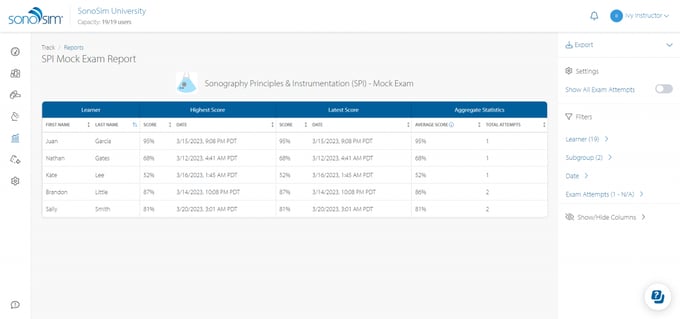
In Reports Hub, under Detailed Reports, the newly introduced “SPI Mock Exam Report” enables instructors to access learners’ mock exam scores. The report displays learners’ highest, latest, and average scores, along with a complete history of all scores and dates, which can be viewed by toggling the “Show All Exam Scores” option.